
IBC tanks, or Intermediate Bulk Containers, play a crucial role in the storage and transportation of liquids and granulated materials across various industries. As the demand for these versatile containers continues to grow, manufacturers face the challenge of delivering high-quality products efficiently and at scale. The key to meeting this demand lies in a well-structured and comprehensive IBC tank manufacturing process. In this article, we will delve into each stage of this process, from handling raw materials to delivering refined IBC tanks, to understand the intricacies and innovations behind the scenes.

1. Raw Materials and Material Handling:
The foundation of every IBC tank begins with the selection of appropriate raw materials. Manufacturers carefully choose high-grade plastics, such as HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) or LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene), to ensure durability and suitability for various contents. These raw materials undergo a rigorous quality check and are stored in controlled environments to preserve their integrity.
Material handling is a critical step to ensure a smooth production process. Automated systems transport the raw materials to the extrusion blow molding machine, where they are accurately measured and fed into the processing unit. Proper material handling minimizes wastage and enhances overall efficiency.


2. Extrusion Blow Molding Machine:
At the heart of the IBC tank manufacturing process lies the extrusion blow molding machine. This sophisticated piece of equipment is responsible for shaping the IBC tank exteriors with precision and consistency.
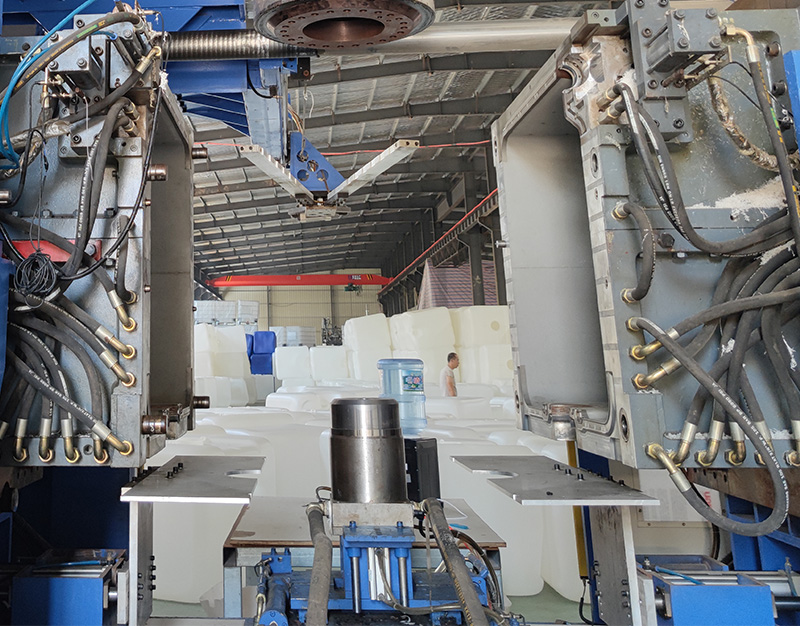
The process begins with the heating of the raw material, which is then melted and extruded into a parison, a hollow tube-like structure. The parison is placed into a mold, and compressed air is introduced to expand and shape it into the desired form. The mold defines the tank's dimensions and features, and intricate designs can be achieved through advanced mold engineering.
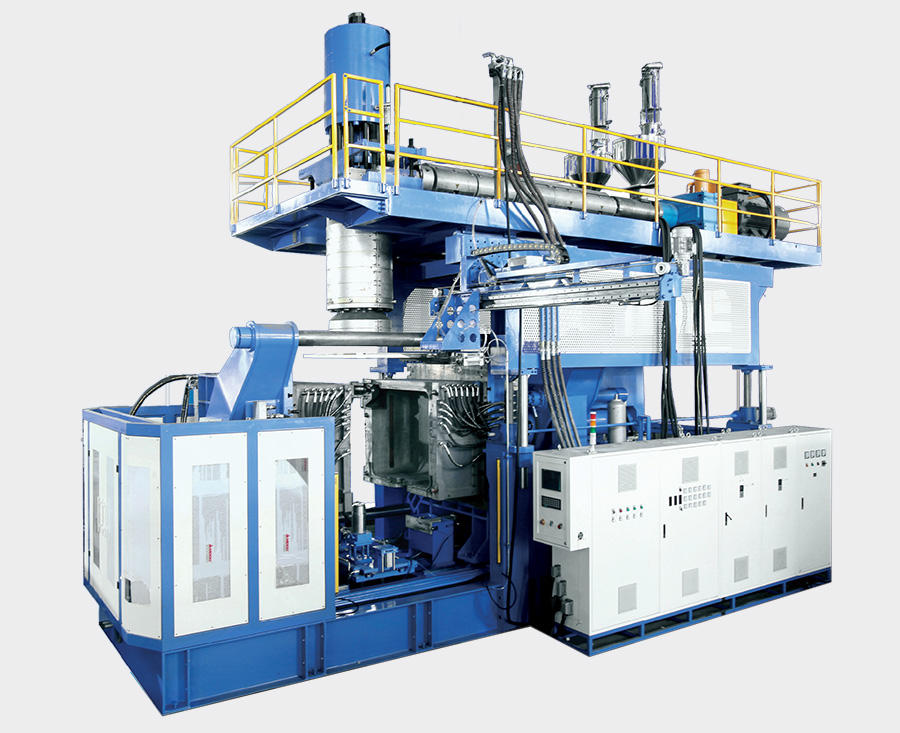


Here is a list of auxiliary equipment that can be used in the IBC blow molding process:
- [ ] Chiller: Used for cooling the IBC tanks after blow molding to ensure product dimensional stability and surface quality.
- [ ] Material Loader: Helps in conveying plastic raw materials to the blow molding machine for processing.
- [ ] Material Dryer: Removes moisture from plastic resins to prevent defects in the blow-molded products.
- [ ] Mold Temperature Controller: Maintains precise and consistent mold temperatures, ensuring uniform product quality.
- [ ] Conveyor System: Transports the blow-molded IBC tanks from the machine to subsequent processing or packaging stages.
- [ ] Leak Testing Machine: Inspects the integrity of the blow-molded IBC tanks to ensure they are leak-free and meet quality standards.
- [ ] Automatic Deflashing Machine: Removes excess flash and trim from the blow-molded products, enhancing their appearance and functionality.
- [ ] Material Mixer: Ensures consistent blending of colorants and additives with the plastic resins for uniform product coloring.
- [ ] Labeling Machine: Applies labels or identification marks to the blow-molded IBC tanks for easy identification and branding purposes.
- [ ] Robotic Handling System: Automates the handling and stacking of blow-molded IBC tanks, improving production efficiency and reducing labor requirements.
- [ ] Scrap Grinder: Recycles any rejected or excess plastic materials generated during the blow molding process.
These auxiliary machines complement the main blow molding machine, enhancing the efficiency, quality, and overall productivity of the IBC tank manufacturing process.
3. Mold Design and Manufacturing:
Mold design is a critical aspect of the IBC tank production process. Manufacturers must consider factors like material flow, cooling, and ejection to achieve uniform thickness and prevent defects in the final product. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and simulation software aid in creating molds that meet precise specifications.
The mold manufacturing process involves precision engineering and high-quality materials. Aluminum or steel is commonly used for mold construction, ensuring durability and the ability to withstand repeated molding cycles. The development of high-performance molds enables manufacturers to produce IBC tanks with consistent quality and dimensional accuracy.


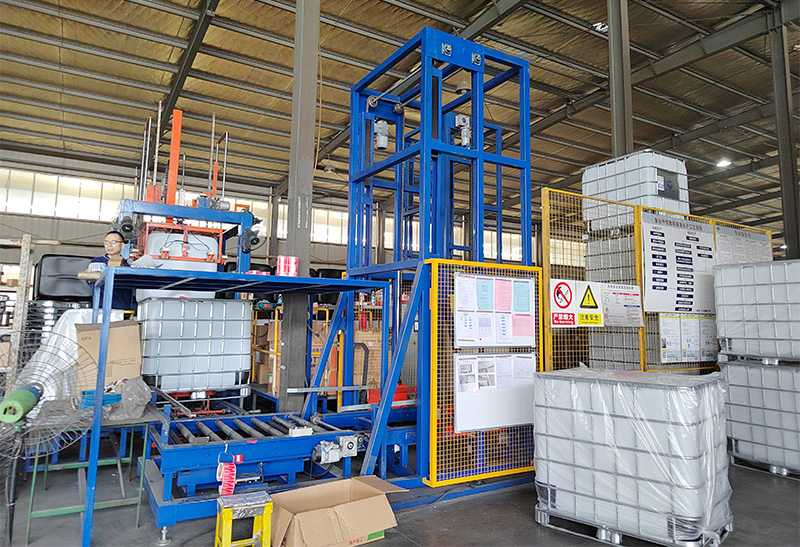
4. Frame Production Line:
In tandem with the blow molding process, the frame production line plays a crucial role in creating sturdy and reliable support structures for IBC tanks. The frames, typically made of galvanized steel, reinforce the tanks' structure and provide added protection during handling and stacking.
The frame production line involves precision cutting, welding, and assembly processes to create frames tailored to specific IBC tank dimensions. The integration of the frame with the blow-molded tank ensures a secure and durable final product, capable of withstanding the demands of industrial use.
In the IBC frame production line, the following machines and equipment are used, along with their respective functions:
(1) Vertical Cutting Machine: Used to cut metal sheets into the appropriate length and width suitable for IBC frame production.
(2) Bending Machine: Used to bend the metal sheets according to the predetermined angles and shapes required for the IBC frame components.
(3) Welding Machine: Performs the welding process to join the bent metal components together and form the IBC frame structure.
(4) Surface Treatment Equipment: This includes processes like sandblasting, priming, and painting, which enhance the IBC frame's corrosion resistance and appearance.
(5) Inspection and Quality Control Devices: These machines are used to ensure the dimensional accuracy and structural integrity of the finished IBC frames, meeting safety and quality standards.
(6) Conveyor System: Transports the IBC frame components between different stages of the production line for efficient assembly and processing.
(7) Automated Handling Equipment: Facilitates the movement and positioning of IBC frame components during the manufacturing process, increasing production efficiency and reducing manual labor.
(8) Automatic Valve Cap Tightening Machine: This machine is specifically designed to automatically tighten the valve caps onto the IBC tanks securely. It ensures a consistent and proper seal, preventing any leakage or spillage during transportation and storage of the IBC tanks. The automatic valve cap tightening machine streamlines the assembly process, significantly improving production efficiency and reducing the need for manual labor.
The combination of these machines and equipment in the IBC frame production line allows for precise and efficient manufacturing of sturdy and reliable frames, meeting the diverse needs of various industries.

6. Production Line for Other Plastic Components:
Apart from the inner tank, IBC tanks consist of various plastic components that play vital roles in ensuring their functionality and usability. These plastic parts include corner protectors, valves, caps, and fittings. The production line for these components involves several key steps:

In the Production Line for Other Plastic Components, two injection molding machines are required - 240T injection molding machine and 170T injection molding machine. These machines play a crucial role in manufacturing various plastic components for IBC tanks, such as corner protectors, drum covers, valve caps, and other fittings.
v 240T Injection Molding Machine: This machine has a clamping force of 240 tons and is capable of injecting larger volumes of molten plastic into the molds. It is utilized for producing larger and more complex plastic components, such as the main body of corner protectors and drum covers.
v 170T Injection Molding Machine: With a clamping force of 170 tons, this machine is used for manufacturing medium-sized plastic components with high precision and consistency. It is suitable for producing components like valve caps and smaller fittings.
Both injection molding machines operate by heating plastic pellets to a molten state and injecting the molten material into molds, where it solidifies and takes the desired shape. The injection molding process ensures excellent repeatability, allowing for the consistent production of high-quality plastic components that meet stringent industry standards.

By having a combination of 240T and 170T injection molding machines in the production line, manufacturers can efficiently produce a wide range of plastic components needed for assembling IBC tanks, catering to various customer specifications and applications. This enables them to offer a comprehensive and reliable solution for IBC tank production, meeting the diverse demands of their customers across different industries.
The complete IBC tank production process involves not only the main blow molding machine for the inner tank but also several other vital production lines. These include the frame production line, which ensures the tanks' stability and handling, and the line for other plastic components, which provide essential functionalities to the IBC tanks.
By integrating advanced technologies, skilled craftsmanship, and quality control measures in each production line, manufacturers can produce IBC tanks that excel in reliability, performance, and safety. The continuous pursuit of innovation and adherence to industry standards ensure that IBC tanks remain a trusted solution for diverse material handling and storage needs across various industries. As customer demands evolve, the IBC tank production process will continue to evolve, delivering even more efficient, sustainable, and versatile solutions for modern material transportation challenges.
5. Quality Assurance and Testing:
As IBC tanks are used to transport a wide range of valuable and hazardous materials, stringent quality assurance measures are essential. Manufacturers conduct thorough testing at various stages of production to ensure the tanks meet industry standards and safety regulations.
Leak testing is a critical aspect of quality assurance, ensuring that the IBC tanks are completely sealed and leak-proof. Dimensional checks and stress testing verify the structural integrity of the tanks, ensuring they can withstand the rigors of transportation and handling.
10. The Future of IBC Tank Manufacturing:
The IBC tank manufacturing industry continues to evolve with ongoing research and technological advancements. Innovations in material science, blow molding techniques, and automation systems hold the promise of further enhancing the efficiency, quality, and sustainability of IBC tank production.
As customer demands evolve and industries seek safer, more efficient solutions for material handling and storage, IBC tank manufacturers must continue to adapt and innovate, ensuring their place at the forefront of this critical industry.
The production of IBC tanks is a highly intricate process that involves a well-orchestrated assembly of technologies, expertise, and quality assurance measures. From selecting raw materials to delivering refined products, each step contributes to creating IBC tanks that meet the diverse needs of various industries.
As manufacturers embrace cutting-edge technologies, automation, and sustainable practices, the future of IBC tank manufacturing promises to be even more efficient, reliable, and environmentally responsible. With a commitment to precision and continuous improvement, the industry will continue to thrive, providing essential solutions for modern material storage and transportation challenges.

















